
Value –> Price
The value of a product is determined by its capacity to fulfill human desires, and furthermore, the true value is contingent on the product’s usefulness in its least significant application, known as marginal utility.
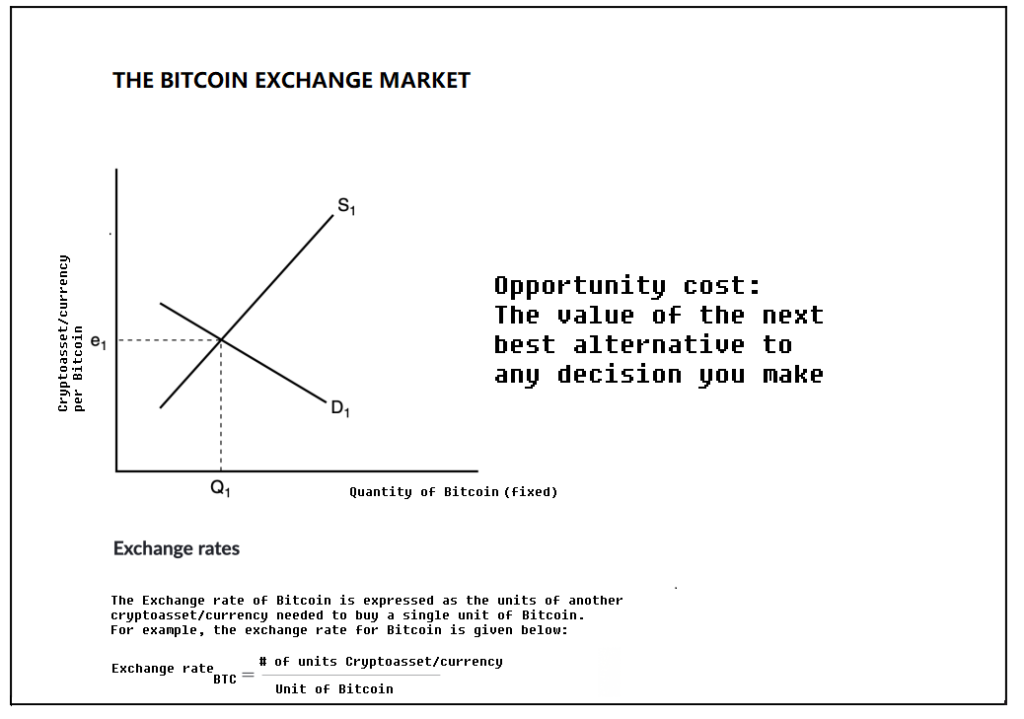
The supply and demand dynamics of Bitcoin (BTC) play a pivotal role in its price trajectory. One major event that impacts these dynamics is the Bitcoin halving, which takes place approximately every four years. To grasp this concept fully, Let’s break down the concepts of supply and demand, dive into the outcomes of a Bitcoin halving event, and explore the factors that influence supply and demand.
Supply and Demand for Bitcoin:
Supply: Bitcoin boasts a fixed supply cap of 21 million coins. This implies that there will never exist more than 21 million Bitcoins. This restricted supply stands in stark contrast to traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed by central banks, potentially leading to inflation. The assured and limited supply of Bitcoin constitutes one of its fundamental attributes.
Demand: The demand for Bitcoin is driven by an array of factors, including its role as a store of value, a medium of exchange, unit of account and speculation by investors. Factors such as institutional adoption, regulatory developments, and macroeconomic conditions also exert their influence on demand.
Bitcoin Halving: The Bitcoin halving is an event that transpires approximately every 210,000 blocks, or roughly every four years. During this event, the reward that miners receive for validating transactions and appending them to the blockchain is halved. In Bitcoin’s nascent stages, miners were rewarded with 50 BTC per block. After the initial halving, this figure decreased to 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, 6.25 BTC, 3.125 BTC, and so on.
By the way, please have a look here: https://mempool.space/ and explore information about the next predicted block, the most recently mined block along with its timestamp, block number, the total number of transactions, and transaction fees.
It’s worth noting that each block successfully mined by a miner is rewarded with the current sum of 6.25 BTC in addition to the collected transaction fees. Read more here
Impact on Supply and Demand:
Impact on Supply:
Supply Reduction: The Bitcoin halving diminishes the rate at which new Bitcoins are generated, effectively curbing the supply introduced into the market. This event enforces scarcity, mirroring the mining of precious resources like gold. Consequently, the supply of new Bitcoins is reduced by 50%, potentially leading to decreased selling pressure from miners.
Lost Bitcoins: Over time, a substantial number of Bitcoins have been lost due to forgotten private keys or inaccessible wallets. These misplaced Bitcoins effectively shrink the circulating supply, augmenting the value of each remaining Bitcoin slightly.
Whale Holdings: The circulating supply of Bitcoin can be affected by large holders (whales) who may opt to move or “hodl” their coins. The decisions made by these whales can exert an influence on supply dynamics.
Miner Holdings: Miners, who earn fresh Bitcoins, confront the decision of either selling them to cover expenses or holding them as an investment. The behavior of miners influences the pace at which new supply infiltrates the market.
- Mining Difficulty: Bitcoin’s network adjusts its mining difficulty approximately every two weeks to ensure that new blocks are mined, on average, every ten minutes. If the total hash rate increases significantly (more mining rigs or better “new” mining rigs), the network may respond by increasing the mining difficulty. As a result, miners need to invest more computational power and resources to validate transactions and earn rewards. This can lead to increased operational costs for miners, which may affect their selling behavior. They might need to sell more of their newly minted Bitcoins to cover expenses, potentially increasing selling pressure on the market.
Exchange Reserves: The quantity of Bitcoin stashed in the wallets of cryptocurrency exchanges can impact supply. A reduction in exchange reserves might signal that users are transferring their Bitcoins to cold storage for long-term retention.
Companies (Public and Private): The quantity of Bitcoin stashed in the wallets of companies can impact supply.
Fund/ETF Reserves: The quantity of Bitcoin stashed in the wallets of cryptocurrency funds and ETFs can impact supply.
Government entities: The quantity of Bitcoin stashed in the wallets of governments can impact supply.
Bitcoin locked in contracts (Layer 2s and other blockchains):
The quantity of Bitcoin stashed in the wallets of Layer 2s and other blockchains can impact supply.
Forks and Airdrops: Forks, where a new cryptocurrency is spawned based on the Bitcoin blockchain, can affect the supply. Bitcoin holders may receive an equivalent amount of the new cryptocurrency, affecting their decisions to buy, sell, or retain both assets.
Impact on Demand:
Retail Adoption: As more merchants and businesses embrace Bitcoin as a payment method, its utility as a medium of exchange expands. Enhanced utility can stimulate demand from consumers keen on employing Bitcoin for transactions.
Institutional Adoption: A surge in participation by institutional investors and financial institutions can galvanize significant demand for Bitcoin. High-profile investments by companies have catapulted Bitcoin into the spotlight as a potential store of value and hedge against inflation.
Market Sentiment: News events, trends on social media, and public sentiment have the potential to drive mainstream adoption, sparking interest and increasing demand among both retail and institutional investors. Positive developments, regulatory clarity, or endorsements from influential figures can trigger FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) and amplify buying interest.
Cross-Border Transactions: Bitcoin can be utilized for cross-border transactions, offering a more cost-effective and expeditious alternative to traditional remittance services. Demand may surge in regions burdened by substantial remittance volumes.
Peer-to-Peer Trading: Peer-to-peer (P2P) trading platforms empower individuals to directly buy and sell Bitcoin. P2P trading can constitute a noteworthy source of demand, particularly in countries grappling with regulatory constraints.
Education and Awareness: As individuals become more enlightened about BTC and its potential advantages, it can result in heightened demand across a wider spectrum of the populace.
Macroeconomic Factors: Economic conditions, inflation rates, and currency stability in various nations can trigger demand for Bitcoin. In regions grappling with economic uncertainty or hyperinflation, some individuals turn to Bitcoin as a hedge against currency devaluation. In areas where traditional banking services are scarce, Bitcoin can serve as a financial lifeline.
- Global Events: Geopolitical events like capital controls, political upheaval, or trade disputes can boost demand for Bitcoin in regions ensnared by the ramifications of these events.
- Global Economic Events: Major economic upheavals such as recessions or financial crises can influence demand for Bitcoin as investors explore alternative assets that exhibit a low correlation with traditional markets.
- Regulatory Changes: Regulatory determinations and governmental cryptocurrency policies can wield influence on demand. Clear and favorable regulations can invigorate adoption, while restrictive regulations can dampen demand. Remember it is not possible to ban Bitcoin it will keep making blocks.
- Security and Trust: A higher hash rate is generally associated with increased network security. A robust and secure network can boost confidence among investors, potentially attracting more institutional and retail participants.
- Network Health: A consistently high hash rate suggests a healthy and active mining ecosystem. A robust network can handle a higher volume of transactions and provide faster confirmation times.
- Mining Centralization: While a growing hash rate can indicate network health, it may also highlight the centralization of mining power. If a small number of mining pools or entities control a significant portion of the hash rate, it can raise concerns about network security and decentralization.
Technological Advances: Advances in blockchain technology, such as layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network) designed to enhance scalability and diminish transaction fees, make Bitcoin more appealing for diverse use cases, potentially intensifying demand. Lightning Network transactions allows sending milisatoshis (MSAT), which opens up for micropayments for people and connecting IoT(Internet of Things). Partnerships between cryptocurrency payment providers and retailers can elevate demand by streamlining the utilization of Bitcoin.
DeFi Integration: The integration of Bitcoin into decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and protocols can spawn new applications and heightened demand. For instance, Bitcoin can serve as collateral for loans or liquidity pools within the DeFi ecosystem.
Scarcity Perception: The fixed supply of 21 million coins and the digital scarcity narrative associated with Bitcoin can captivate investors seeking an asset deemed to possess a store of value.
Speculation: Speculative trading and investor sentiment exert substantial sway over demand. Traders and investors frequently enter or exit the market based on price trends and their expectations concerning future price movements.
It is paramount to recognize that these influences are interconnected and can vary in significance over time. The Bitcoin market is highly dynamic and subject to a wide range of factors. It’s also worth noting the derivatives markets such as the futures and options markets, and having some understanding of OTC (Over-The-Counter) markets can be beneficial. Traders and investors should meticulously scrutinize these factors to make informed decisions.
In conclusion, the supply and demand dynamics of Bitcoin, in tandem with the phenomenon of halving, constitute pivotal drivers of its price oscillations.
Powered by BTCPayWall